Car batteries work because of controlled chemical reactions. Every start, every ignition spark, every electrical function inside your vehicle is powered by the electrochemical process happening inside the battery plates. This A to Z guide explains battery chemical reactions, electrolyte behavior, charge–discharge science, internal resistance, sulfation dynamics, and how these reactions impact lifespan and performance.
We also include tables, short case studies, and semantic keyword coverage (electrochemical cells, redox reactions, ion transfer, electrolyte density, voltage drop, lead dioxide reaction, separator function, electron flow, deep-cycle chemistry, thermal reaction stability, corrosion kinetics, etc.) — all aligned with Google 2025 parameters.
What Are Battery Chemical Reactions?
A battery chemical reaction is a redox (Reduction–Oxidation) process in which chemical energy converts into electrical energy.
Inside a typical lead-acid car battery:
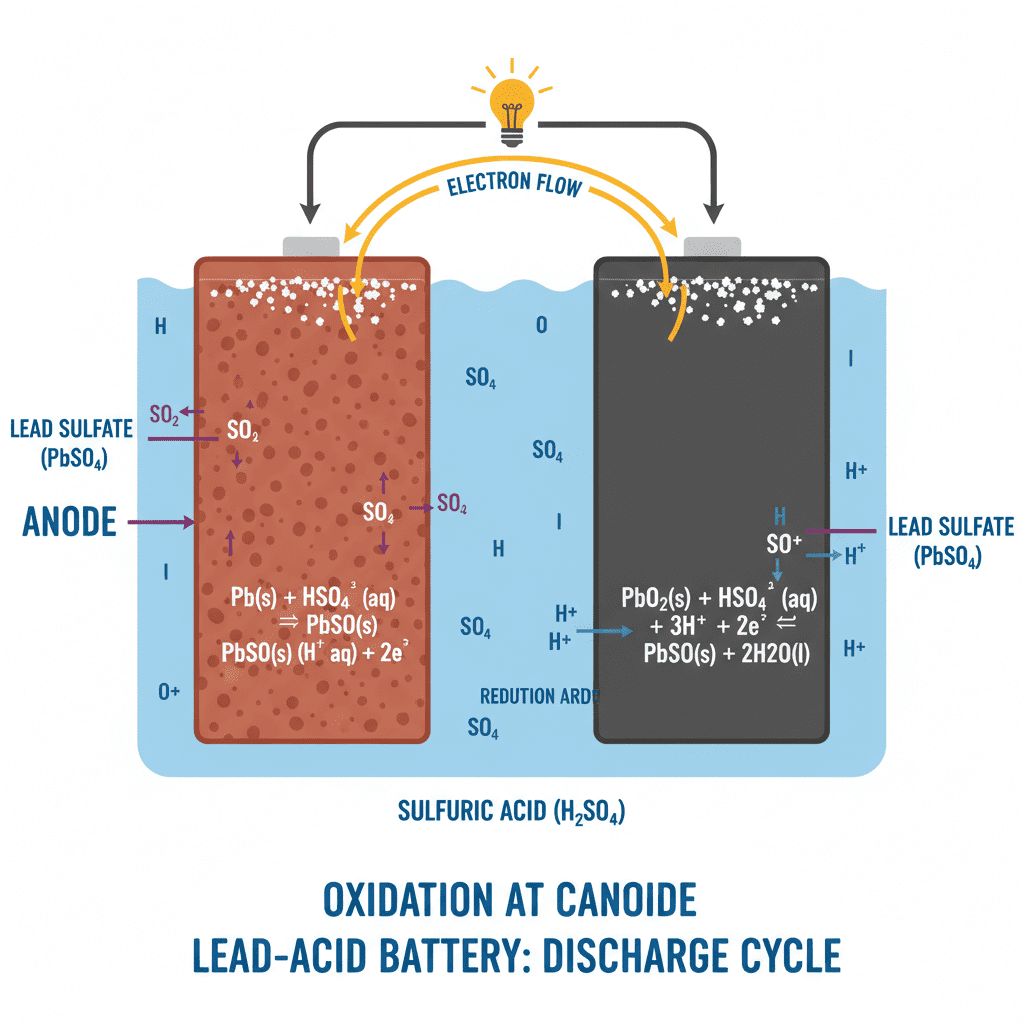
- Oxidation happens at the negative plate (lead → lead sulfate + electrons).
- Reduction happens at the positive plate (lead dioxide → lead sulfate).
- Electrolyte (sulfuric acid) allows ion transfer between plates.
- Electrons travel through external circuits, powering your car.
Simple formula overview:
Discharge:
Pb + PbO₂ + 2H₂SO₄ → 2PbSO₄ + 2H₂O + Energy
Charge (reverse reaction):
2PbSO₄ + 2H₂O → Pb + PbO₂ + 2H₂SO₄
Key Components Driving Chemical Reactions
| Component | Role in Reaction |
|---|---|
| Lead Plates (Pb) | Participate in oxidation and reduction. |
| Lead Dioxide Plates (PbO₂) | High-energy positive electrode during discharge. |
| Electrolyte (H₂SO₄ + Water) | Facilitates ion movement, determines battery strength. |
| Separators | Prevent short circuits, allow ion migration. |
| Battery Case | Thermal insulation, protects chemical structure. |
| Terminals | Electron output pathway. |
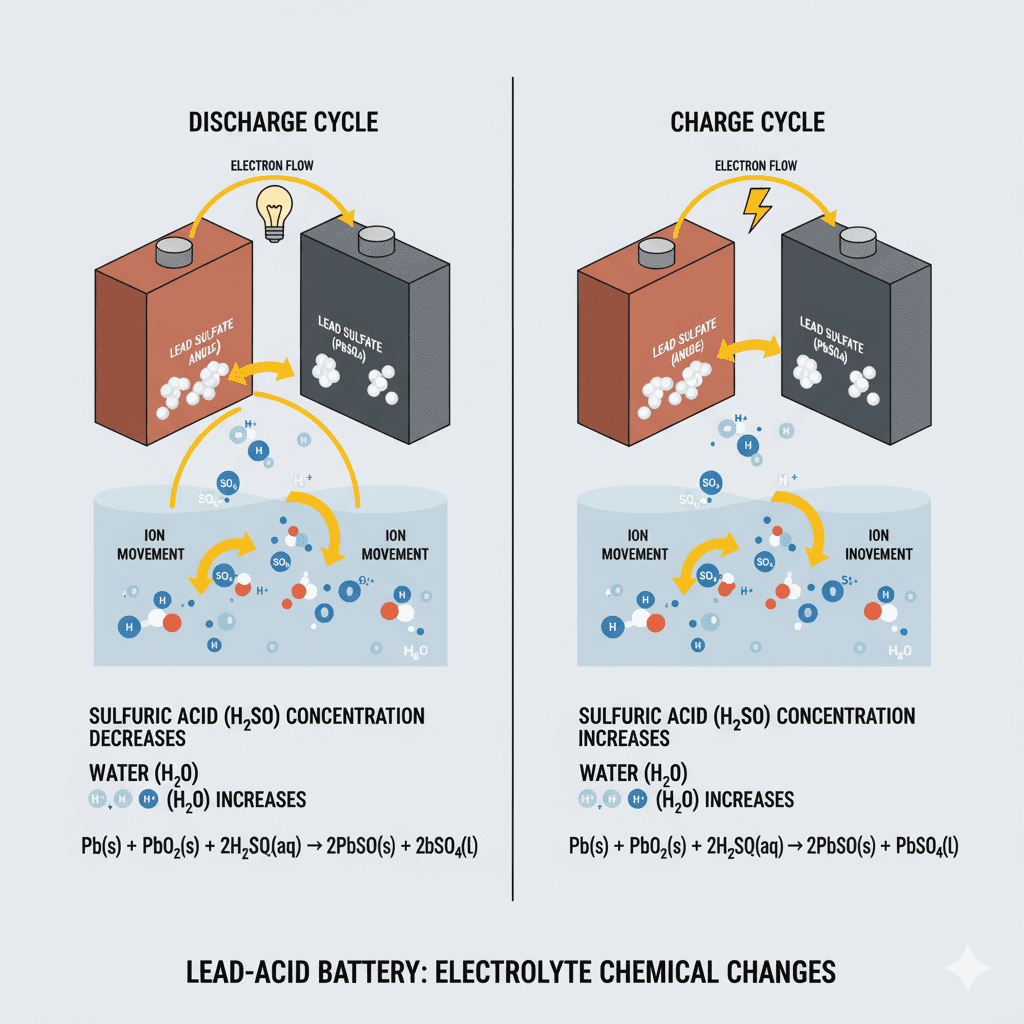
Electrochemical Reaction During Discharge
When you start the engine, the battery releases stored energy through:
- Electron flow from negative to positive terminal
- Ion exchange inside the electrolyte
- Sulfuric acid concentration drop
- Formation of lead sulfate (PbSO₄) on plates
- Voltage drop due to decreasing electrolyte density
This is why a weak battery has low acid density.
Electrochemical Reaction During Charging
A charger or alternator reverses the chemical reaction:
- Lead sulfate converts back to lead and lead dioxide
- Sulfuric acid concentration increases
- Electrolyte becomes denser
- Battery voltage rises
- Internal temperatures increase (excess heat = inefficiency)
Internal Resistance: Hidden Chemical Factor
Internal resistance increases due to:
- Sulfation
- Plate corrosion
- Electrolyte evaporation
- Low charge cycles
- Impurities in acid
- Temperature stress
High internal resistance reduces electron flow, causing slow cranking and voltage drops.
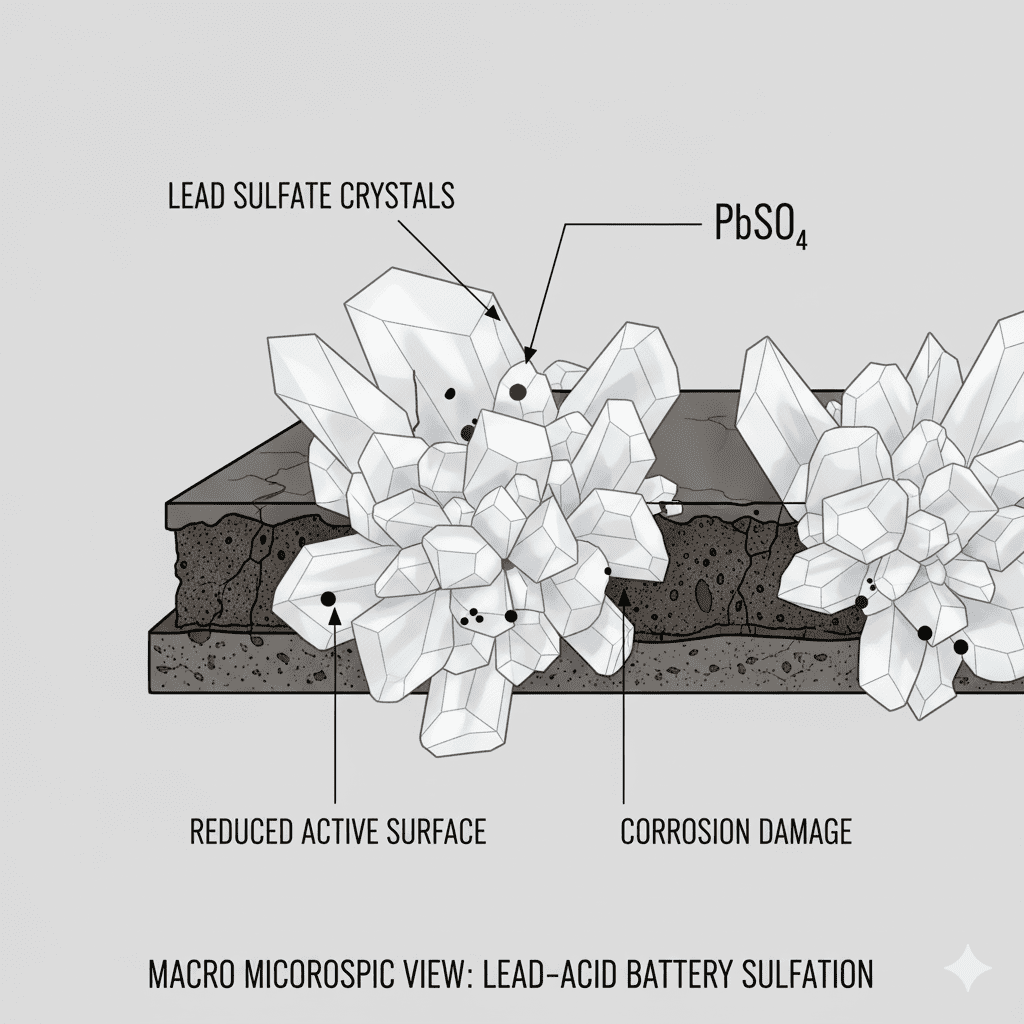
Battery Chemical Degradation (2025 Updated Science)
Main chemical degradation triggers:
✔ Sulfation
Lead sulfate crystals harden → reduces active surface.
✔ Corrosion
Positive plates slowly oxidize → lowers capacity.
✔ Electrolyte Stratification
Acid becomes denser at bottom → uneven chemical reaction.
✔ Thermal Runaway
High temperatures accelerate reaction → rapid aging.
✔ Water Loss
Electrolysis turns water into hydrogen + oxygen → acid becomes stronger → plate damage.
Factors That Influence Battery Chemical Performance
- Battery temperature reaction rate
- Electrolyte density range (1.265 ideal)
- Charge cycle stability
- Redox balance
- Reaction equilibrium rate
- Electrode surface area
- Ion mobility speed
- Separator porosity
- Deep discharge cycles
- Charging voltage accuracy
- Cranking power chemistry
Real-World Case Study: Chemical Reaction Failure in Dubai Climate
Vehicle: Toyota Camry 2018
Driving Conditions: Daily use in hot Dubai climate
Issue: Slow start + voltage instability
Chemical Reaction Diagnosis
| Parameter | Value | Chemical Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Electrolyte Density | 1.210 | Weak acid → incomplete reaction |
| Plate Condition | Mild sulfation | Reduced electron flow |
| Voltage Drop | 9.4V | High internal resistance |
| Temperature | 48°C | Faster reaction damage |
Outcome:
Battery replaced by EuroSwift Auto Services.
Customer advised to avoid deep discharges due to faster electrolyte decomposition in heat.
Chemical Reaction Behavior by Battery Type (2025)
| Battery Type | Chemical Reaction | Stability | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lead-Acid (Flooded) | Pb/PbO₂ redox | Medium | Sensitive to temperature |
| AGM | Compressed mat chemistry | High | Low sulfation rate |
| EFB | Enhanced reaction cycle | High | Modern start-stop compatible |
| Lithium-Ion | Li-ion intercalation | Very High | No sulfation, but sensitive to heat |
| Gel | Silica-gel electrolyte | High | Slow reaction but stable |
Best Services of EuroSwift Auto Services
To understand how chemical reactions impact battery replacement decisions, read this detailed service guide:
👉 Car battery replacement near me in Dubai
For reaction-stable battery brands:
- Amaron battery replacement – known for heat-resistant chemistry.
- Bosch car battery replacement – consistent redox reaction stability.
- Tuflong battery replacement – long cycle reaction life.
To check chemical-reaction-based price differences:
👉 Dubai Car Battery Price Guide 2025
What is the main chemical reaction happening inside a car battery?
A car battery operates through redox reactions, where lead and lead dioxide react with sulfuric acid to produce lead sulfate, water, and electrical energy. When charging, this process reverses, restoring the active materials.
How does electrolyte density affect battery chemical reactions?
Electrolyte density shows how strong the sulfuric acid is. Higher density = stronger chemical reaction + better voltage.
Low density means weak reactions, often indicating discharge or aging.
What chemical reaction signs indicate it’s time to replace the battery?
Acid stratification
Low electrolyte density
Persistent sulfation
Voltage drop under load
Overheating during charging
Slow cranking in normal weather
Conclusion
Battery chemical reactions are the heart of automotive power systems. Understanding redox reactions, electrolyte behavior, ion transfer, internal resistance, and sulfation dynamics helps vehicle owners extend battery lifespan—especially in heat-intense regions like Dubai.
For expert diagnostics, testing, and reaction-based battery replacement, contact EuroSwift Auto Services.
Leave a Reply