The alternator is the most important component in a vehicle’s electrical system after the battery. Its job is simple but critical: keep the battery charged and power all electrical components while the engine runs. Without a properly functioning alternator, even a brand-new battery will die within minutes.
This guide explains exactly how the alternator charges the battery, how it works internally, symptoms of failure, testing, maintenance, and real-world diagnostic data—based entirely on the keyword topic.
How the Alternator Charges the Battery
When the engine starts, the battery provides the initial current to turn the starter motor. Immediately after ignition, the alternator takes over.
1. Mechanical Power Converts to Electrical Power
The alternator is linked to the engine through the serpentine belt. As the engine rotates, the alternator spins and begins generating power.
2. Alternator Produces AC Electricity
The internal rotor spins through copper windings (stator), creating alternating current (AC).
3. AC Is Converted to DC
A rectifier inside the alternator converts AC into DC power, which is safe for the battery.
4. Voltage Regulator Controls Output
To protect the battery, the voltage regulator ensures charging voltage stays between 13.8V and 14.7V.
5. Battery Receives Charging Current
The DC current flows directly to the battery’s positive terminal, restoring its energy.
Why the Alternator Is Essential for Battery Life
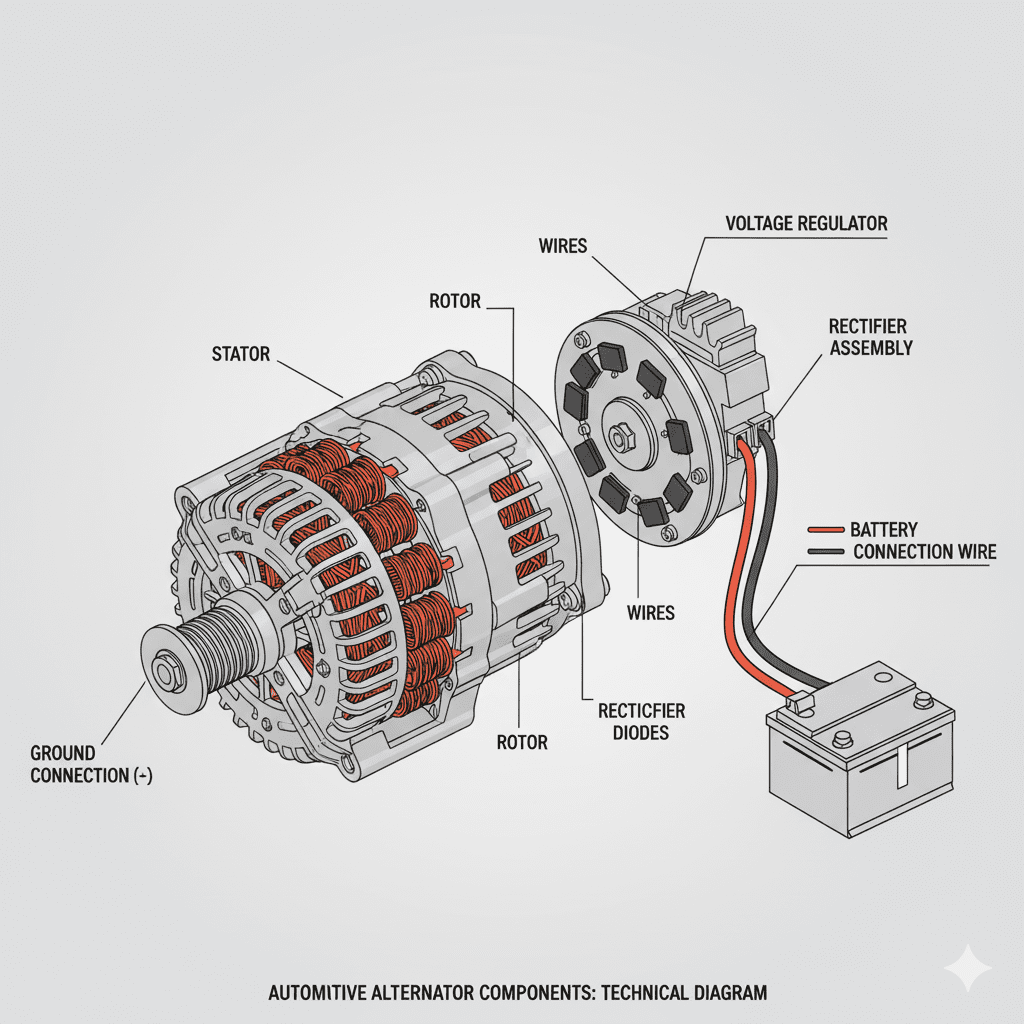
- Maintains battery charge after every start
- Supplies power to lights, AC, infotainment, ECU
- Prevents battery sulfation caused by undercharging
- Protects electronics by regulating voltage
- Ensures stable engine operation
When alternator output weakens, the battery is forced to supply continuous power, leading to premature failure.
Signs the Alternator Is Not Charging the Battery
- Dashboard battery light on
- Dim or flickering headlights
- Burning smell from slipping belt
- Clicking noises or weak cranking
- Car shuts down while driving
- Frequent dead battery
- Voltage below 13.8V when engine is running
Any of these symptoms requires immediate inspection.
Testing Alternator Charging Output
Use a digital multimeter:
| Condition | Ideal Voltage |
|---|---|
| Engine OFF | 12.6V (healthy battery) |
| Engine ON | 13.8V – 14.7V |
| Above 15V | Overcharging (dangerous) |
| Below 13.5V | Undercharging (alternator issue) |
If the voltage stays low, the alternator is not charging properly.
Case Study: Alternator Undercharging Issue in Dubai
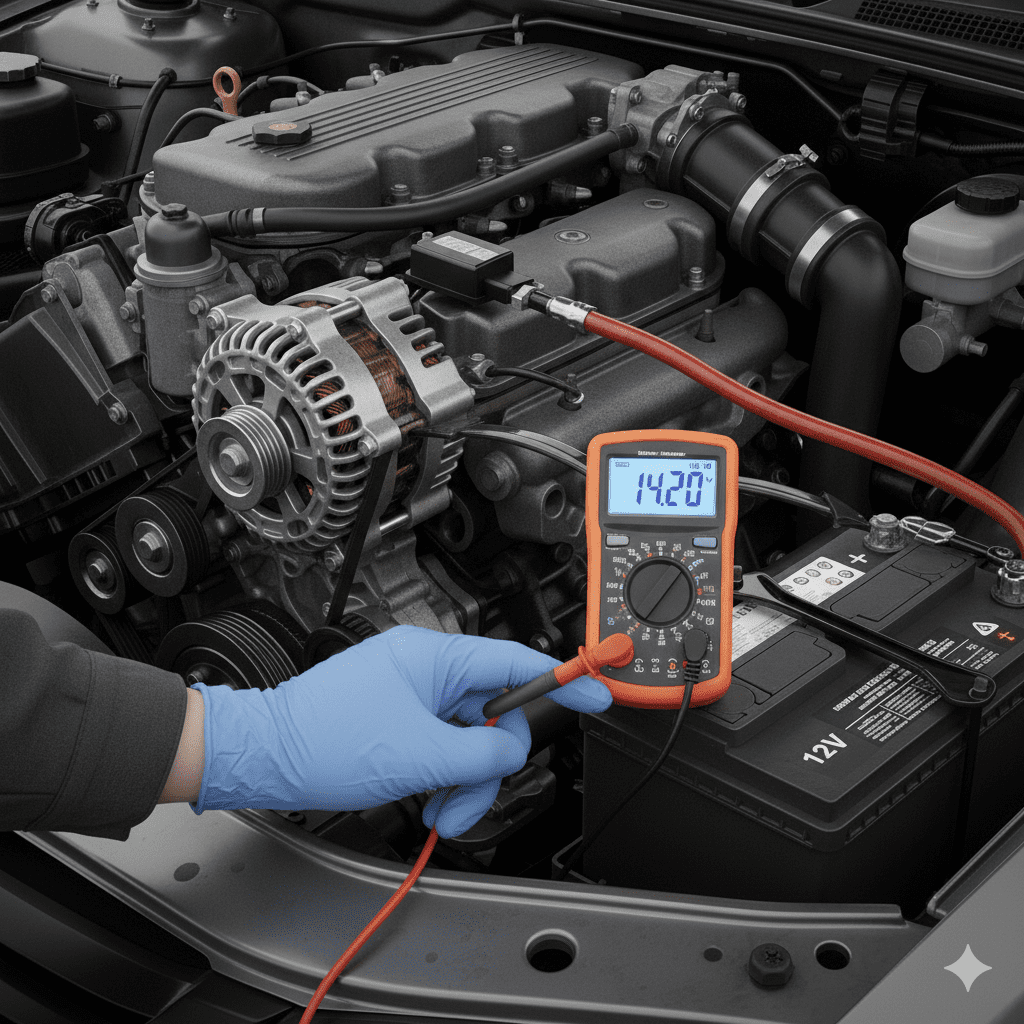
Vehicle: 2020 Nissan Patrol
Issue: Battery dying every 48 hours
Diagnosis at EuroSwift Auto Services
- Battery voltage engine ON: 12.9V (undercharging)
- Alternator regulator not maintaining stable output
- Battery showing early signs of sulfation
Solution
- Replaced alternator assembly
- Installed Amaron battery for stronger charge acceptance
- Cleaned terminals & upgraded grounding wire
Result
Charging voltage restored to 14.3V, vehicle performance normalized, no repeat failures.
Anchor used naturally:
The team recommended the high-performance Amaron Car Battery Replacement option for better long-term reliability.
Alternator vs Battery Responsibilities
| Function | Alternator | Battery |
|---|---|---|
| Powers electrical components | Yes | Only with engine OFF |
| Provides starting power | No | Yes |
| Charges the battery | Yes | No |
| Runs the car while driving | Yes | No |
Helpful Internal Resources for Better Understanding
Enhance your knowledge and get quick access to expert battery services with these helpful internal guides from EuroSwift Auto Services:
- Explore the full cost breakdown in the Complete Car Battery Price Guide 2025
- Get fast on-site support through car battery replacement near me in Dubai
- Upgrade to premium performance using Bosch car battery replacement
- Improve long-term reliability with Tuflong battery replacement
- Choose high-quality power solutions through Amaron Car Battery Replacement
How does the alternator charge the battery while driving?
The alternator converts mechanical rotation into DC electrical energy and sends it to the battery through the positive terminal. The voltage regulator ensures the charging level stays between 13.8V–14.7V.
How do I know if my alternator is not charging the battery properly?
Common signs include:
Battery light glowing
Dim headlights
Weak acceleration of electrical components
Burning rubber smell
Engine stalling while driving
Battery dying repeatedly
Should I replace the alternator or the battery if the car keeps dying?
If the car dies while driving, it’s usually the alternator.
If the car fails to start, it’s usually the battery.
A quick voltage test confirms the fault.
Conclusion
The alternator is the heart of the vehicle’s electrical system. It ensures the battery stays charged, powers all electronic systems, and prevents sudden breakdowns. A weak alternator directly affects battery health and engine reliability. Regular voltage testing and timely replacement protect your vehicle from major electrical failures.
For expert alternator and battery diagnostics, EuroSwift Auto Services provides Dubai’s trusted and fast automotive solutions.
Leave a Reply