Understanding how car batteries charge and discharge is essential because this cycle decides battery health, voltage stability, and starting power. Below is a clean, focused, highly optimized explanation covering every technical point related to charging mechanism, discharging process, chemical reaction, voltage stages, current flow, sulfation impact, alternator role, and real-world behaviour in Dubai heat.
What Does Charging Mean in a Car Battery?
Charging means storing electrical energy back into the battery.
The alternator sends a controlled DC voltage (13.8V–14.7V) which reverses the internal chemical reaction, restoring charge.
Helpful Resource:
See how professional services ensure proper charging cycles at Car Battery Replacement Near Me in Dubai.
What Is Discharging in a Car Battery?
Discharging means the battery releases stored energy to power:
- Starter motor
- ECU
- Headlights
- A/C blower
- Sensors & electronics
This happens when the engine is off or when the electrical load is higher than alternator output.
Mechanism: How Car Batteries Charge and Discharge
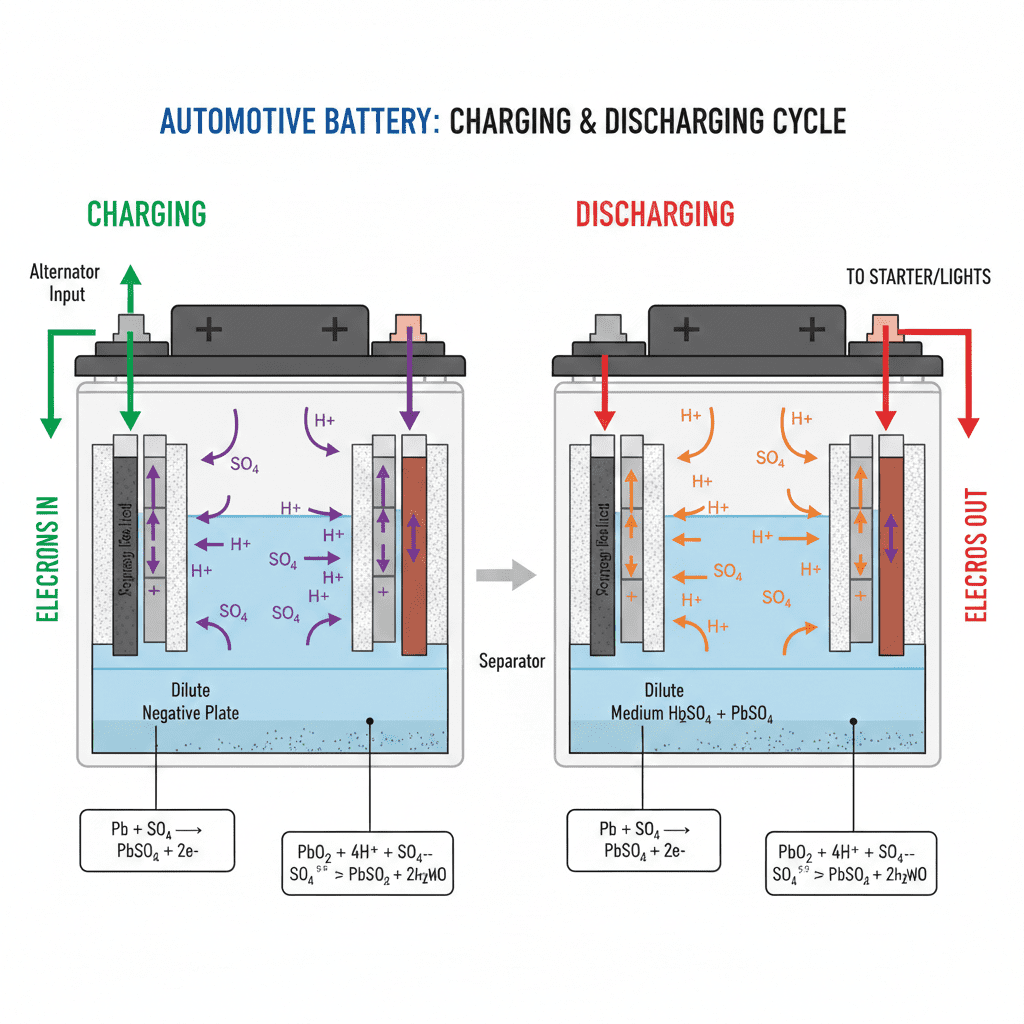
Active Materials
Lead dioxide (positive plate) + lead (negative plate) + sulfuric acid.
Basic Reaction
Charging = reaction reverses.
Discharging = reaction moves forward.
Charging Cycle Steps
- Alternator generates AC.
- Rectifier converts to DC.
- Regulator maintains safe voltage.
- Battery plates restore original chemical state.
- Electrolyte density rises as charge increases.
Discharging Cycle Steps
- Electrical load pulls energy from the battery.
- Electrons flow from negative → load → positive.
- Sulfate coats plates (normal but increases with deep discharge).
- Voltage drops steadily.
Electrolyte Movement
High charge = strong acid.
Low charge = diluted acid.
Flow of Electrons
Discharge: battery supplies current.
Charge: external current pushes electrons back.
Generator (Alternator) Role
Alternator maintains battery charge during driving.
Heat Effect
High temperature increases discharge rate and reduces charge efficiency.
Internal Resistance
Healthy battery = low resistance = faster charging.
Jump-Start Impact
Gives temporary voltage, does not restore chemical capacity.
Key Voltage Levels
| Charge Level | Voltage |
|---|---|
| 100% | 12.6–12.8V |
| 75% | 12.4V |
| 50% | 12.2V |
| Discharged | 11.9V |
Load Effect
More accessories = faster discharge.
Minimal Charge Requirement
Battery needs 20–25 minutes of driving to regain stable charge.
Normal Self-Discharge
1–2% per day in hot climates.
Overcharging
Voltage >14.8V damages plates and overheats the battery.
Plate Sulfation
Undercharging → hard sulfate crystals → lowers charge acceptance.
Quick Charge Behaviour
Alternator charges fast till 70%, then slows down.
Recharge Time
Complete charging takes 1–2 hours of consistent driving.
Sulfation Effect
Worst enemy of charging performance.
Premium brands reduce sulfation:
👉 Amaron Battery Replacement in Dubai
Temperature Influence
High heat = low charging efficiency, high discharge rate.
Undercharging Causes
Short trips, weak alternator, or parasitic drain.
Voltage Regulation
Smart regulators prevent over/under-charging.
Wattage Load Calculation
Higher wattage devices = deeper discharge.
Excessive Drain
Parking mode electronics cause parasitic drain.
Yearly Performance Drop
Dubai climate causes 10–12% decline per year.
Zero Charge Condition
Battery becomes unrecoverable when voltage stays below 10.5V too long.
Case Study: Charging & Discharging Behaviour in Dubai

| Parameter | Car 1 (Long Drive) | Car 2 (Short Trips) |
|---|---|---|
| Daily Running | 40 minutes | 10 minutes |
| End-of-Day Voltage | 12.55V | 12.05V |
| Sulfation Risk | Low | High |
| Battery Life | 2.5 years | 1.3–1.6 years |
Conclusion:
Short drives do not complete the charging cycle → battery remains half-charged → faster discharge → early failure.
Discharge Symptoms (Directly Keyword Connected)
- Slow crank
- Dim lights
- Voltage <12.2V
- Frequent jump-starts
- Weak alternator output
Recommended Batteries for Better Charge/Discharge Cycles
✔ Amaron (Heat-Resistant, Long Life)
Link: Amaron Car Battery Dubai
✔ Bosch (Strong Charge Acceptance)
Link: Bosch Battery Replacement
✔ Tuflong (Stable Discharge Behaviour)
Link: Tuflong Battery Dubai
✔ Battery Price Guide (2025)
👉 Car Battery Price Guide Dubai 2025
How do car batteries charge while driving?
Car batteries charge through the alternator, which converts mechanical energy into electricity. The alternator sends 13.8V–14.7V DC power to the battery, reversing the chemical reaction and restoring lost charge.
What causes a car battery to discharge?
A battery discharges when electrical components like the starter, headlights, ECU, A/C blower, and sensors draw power. Discharge also happens when the vehicle is off due to parasitic drain or heat-related self-discharge.
When should I replace a battery with poor charging performance?
If voltage repeatedly drops below 12.0V, sulfation increases, or the battery fails to hold charge after driving, replacement is recommended.
For reliable replacement, check EuroSwift Auto Services here:
👉 Trusted Car Battery Replacement Near Me Dubai
Conclusion
The charging and discharging cycle determines how long a battery will last and how well it performs.
A healthy electrical system, proper alternator voltage, and stable daily driving patterns ensure the battery stays fully charged.
In regions like Dubai, the charge–discharge balance becomes even more critical due to extreme heat.
For fast, on-site replacement or diagnosis, EuroSwift Auto Services provides:
- 15–20 min arrival
- 100% genuine batteries
- 18-month warranty
- 24/7 service
Leave a Reply