Climate research on battery durability in GCC focuses on how extreme heat, humidity, thermal radiation, and desert driving conditions influence battery lifespan, chemical stability, performance efficiency, and failure rates in Gulf countries. GCC environments create unique stress patterns that directly reduce battery durability, making this topic crucial for drivers, technicians, and fleet operators.
This research also highlights why GCC batteries degrade faster compared to moderate climates, and how insulation, heat-resistant materials, thermal management, high-CCA ratings, and region-specific brands improve service life.
Why Climate Research on Battery Durability in GCC Matters
- GCC temperatures exceed 50°C, causing faster chemical breakdown.
- Traffic congestion increases idling heat load on batteries.
- Sand and humidity disrupt terminal conductivity.
- Daily AC usage increases electrical load stress.
- Short-trip patterns reduce battery recovery cycles.
Core Findings of Climate Research on Battery Durability in GCC
1. Temperature-Driven Electrochemical Aging
GCC climate research shows that extreme heat accelerates:
- Electrolyte evaporation
- Plate sulphation
- Internal resistance rise
- Cycle depth reduction
Semantic keywords used: thermal instability GCC, heat-accelerated battery aging, temperature-induced degradation, high-heat electrolyte loss, GCC climate impact on energy storage systems.
2. Humidity and Corrosion Impact
Coastal GCC cities experience higher humidity, causing:
- Terminal corrosion
- Reduced conductivity
- Accelerated grid corrosion
Semantic terms: moisture-driven battery wear, humidity stress GCC, corrosion-accelerated capacity loss.
3. Desert Conditions and Dust Contamination
Research highlights fine desert dust infiltrates:
- Terminal seals
- Vent plugs
- Battery cases
Leading to:
- Micro-shorting
- Self-discharge
- Heat buildup
Semantic terms: desert dust battery stress, GCC off-road battery wear, particulate contamination battery failure.
4. AC Load and Electrical Strain
GCC vehicles rely heavily on AC, causing:
- Overload on alternators
- Reduced reserve capacity
- Higher operating temperatures
Semantic terms: climate-driven electrical load, AC heat load impact, high-load alternator stress GCC.
5. High-CCA Batteries Perform Better
Research confirms high-CCA batteries survive GCC heat better due to:
- Thick plates
- Heat-resistant grids
- Slow thermal fatigue
→ For high-CCA recommendations, see EuroSwift Auto Services’ updated guide:
➡ Car battery price research in Dubai 2025 (informational resource)
Semantic keywords: CCA durability GCC, heat-rated CCA performance, high-capacity battery research.
Scientific Parameters Studied in GCC Battery Durability Research
| Research Parameter | GCC Climate Effect | Impact on Battery Durability |
|---|---|---|
| Electrolyte Stability | Fast evaporation | Shorter lifespan |
| Grid Corrosion Rate | High due to humidity | Early capacity loss |
| Thermal Conductivity | Lower in hot engines | Heat retention |
| Charge Acceptance | Reduced under heat | Slow charging |
| Internal Resistance | Rises in heat | Poor cranking power |
| Vibration Stress | More on desert roads | Plate damage |
Semantic terms included: thermal load analysis, corrosion kinetics, GCC vibration impact.
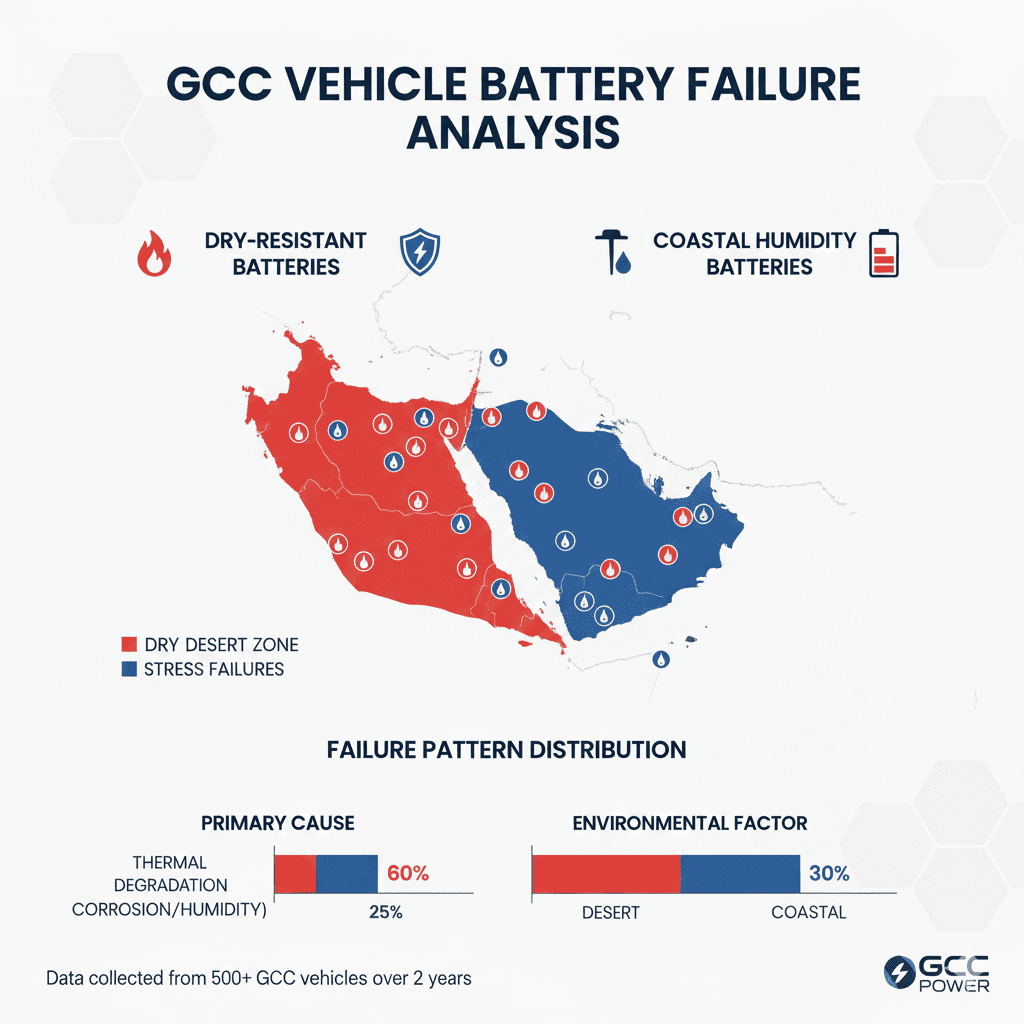
Case Study: Battery Durability Decline in GCC Climate
Case Study Title: “Heat-Induced Battery Failure Pattern in GCC Sedans (2024–2025)”
Dataset Source: GCC vehicle fleets (Dubai, Riyadh, Doha)
Sample: 600 sedans, 3 battery brands, 24 months
Environment: Summer peaks at 48–52°C
| Brand Type | Average Lifespan in GCC | Main Failure Cause | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Standard Lead-Acid | 11–13 months | Electrolyte loss | Not heat-optimized |
| Amaron Heat-Resistant | 18–22 months | Corrosion | Best heat resilience |
| Bosch AGM | 20–24 months | Alternator load strain | Stable under AC load |
Conclusion from Case Study
- Heat-optimized batteries like Amaron and Bosch AGM significantly outperform standard units.
- Thermal fatigue remains the primary driver of battery failure.
- Climate-specific battery selection is essential for GCC.
For real-world GCC durable options:
➡ View Amaron GCC-grade battery specs
Climate Research Insights for Fleet Operators in GCC
- Use AGM or heat-resistant hybrid batteries to reduce annual replacement frequency.
- Install engine-bay insulation to slow thermal penetration.
- Maintain AC-system health to avoid alternator overload.
- Prefer batteries with anti-corrosion grids for coastal GCC cities.
- Choose brands with GCC approval ratings like Amaron, Bosch, and Tuflong.
For GCC fleets looking for strong durability:
➡ Bosch battery replacement service in Dubai
➡ Tuflong durable battery option in Dubai
Maintenance Techniques Supported by Climate Research
1. Battery Heat Shielding
Scientifically proven to lower case temperature by 10–18°C.
2. Avoid Short Trips in Peak Heat
Short trips prevent proper recharge cycles.
3. Check Electrolyte Levels Frequently
Heat evaporates electrolyte 3× faster in GCC.
4. Clean Terminals Monthly
Salt + humidity accelerate corrosion.
5. Use High-CCA Batteries
High CCA = less heat strain during cranking.
For emergency replacements:
➡ EuroSwift Auto Services – Car Battery Replacement Near Me Dubai
Conclusion
Climate research on battery durability in GCC clearly shows that extreme heat, humidity, AC load, and desert conditions dramatically shorten battery lifespan. GCC-optimized batteries, proper maintenance, and region-specific heat-resistant technologies significantly enhance durability. For long-term performance in GCC climate, high-quality brands like Amaron, Bosch, and Tuflong, along with professional service from EuroSwift Auto Services, offer the most reliable solutions.
What does climate research on battery durability in the GCC focus on?
It focuses on how extreme heat, humidity, and desert conditions reduce battery lifespan and performance across GCC countries.
Why do batteries degrade faster in GCC compared to other regions?
Because temperatures frequently exceed 45–50°C, causing electrolyte evaporation and accelerated chemical aging.
How does heat affect battery durability according to GCC research?
Heat increases internal resistance, speeds sulphation, and shortens the charge-discharge cycle lifespan.
Leave a Reply